Price It Right: How Win-Loss Analytics Helped Improve Pricing Strategy
By analyzing won and lost deals, we provided insights for offering the right discounts, resulting in reduced non-standard discounts and improved ARR.
Sep 28, 2020 | Article
Data Visualization: A brief Overview
What is Data Visualization?
Living in this age of Big Data, you would definitely have come across the term “Data Visualization.” It is used by all kinds of people: academics, economists, administrators, CEO’s – you name it! Owing to this popularity, it has so many definitions that when you google “Definition of Data Visualization,” you get about 8,14,00,000 results. Whew! That’s a lot to handle, but don’t worry, we got your back. Simply put, Data Visualization or Data Viz is any visual representation that helps in understanding, organizing, and analyzing data. It helps your numbers tell a meaningful story and helps your readers understand it.
Why do we need it?
A picture is worth a thousand words! This is the mantra behind data viz. According to Danish Physicist Tor Nørretranders, both our conscious and sub-conscious systems process the most information in a given time through vision. This means we are more likely to grasp details from a picture than a text. To illustrate this further, look at the two images below, which lists the processing capacity of our senses.


Even though both images convey the same data, comparing and identifying the largest value is much quicker in the visual representation when compared to the tabular form. So, it goes without saying that when Data is visualized, it becomes easier to understand. Understanding paves the way to better communication, which in turn results in effective utilization of the information.
How does it help us?
A huge incentive of using visuals over text is the sheer amount of data insights it provides. A quicker understanding of data leads to swift actions, which are very important for key decision-makers. Spotting trends and patterns help companies stay ahead of the competition. Finding and correcting errors becomes easier, making the business productive. With its help, Business stakeholders can effectively analyze their reports and focus on the areas requiring attention. In short, Data viz helps in understanding information much faster and in recognizing patterns that might otherwise be difficult to see with the text-based data.
Matching Data to Charts
What information do we need to select a chart?
Data Viz, like any other tool, can be very useful when used right. To get the most out of your data, you need to match your data with the right type of visual chart. How do we do that? By asking yourself the following questions:
1. Who is my audience?
2. What insights do I want my readers to gain?
3. What should be the range of my axis?
4. Should I display values over time or among groups?
5. What information many categories do I need?
6. How many data points do I need for each category?
The Cheatsheet
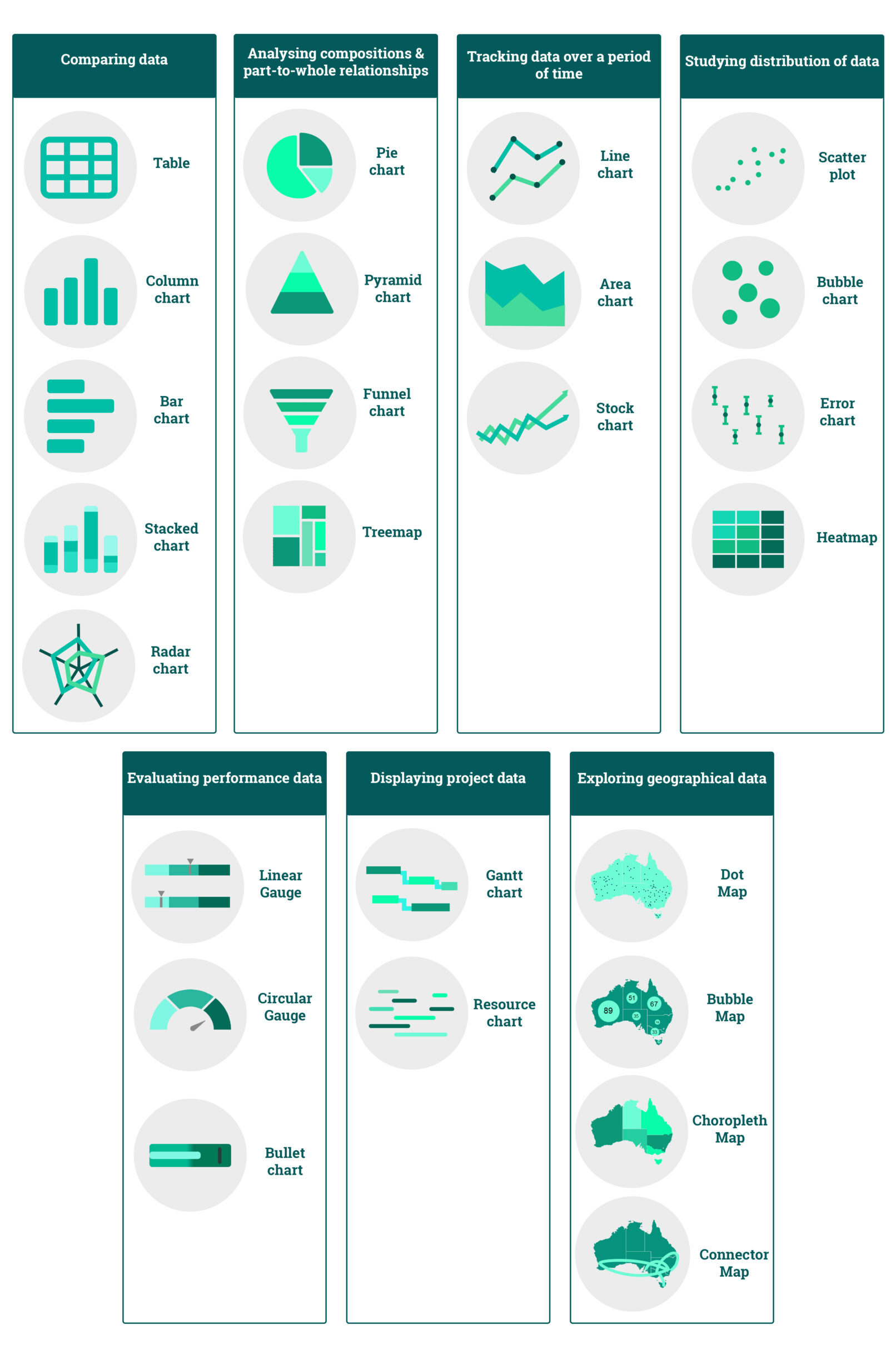
Once you have the answers to the above questions, the next step is to use that knowledge to identify the best chart for you. We have made a table that shows you which visual chart is to be used for which type of visualization task and in which case. Just refer to the following table to find the ideal partner for your data:
Comparing Data
When to Use
Chart Type
Table

Column chart

Bar chart

Stacked chart

Radar chart

Tracking data over a period of time
When to Use
Chart Type
Line chart

Area Chart

Stock Chart

Analyzing compositions and part-to-whole relationships
When to Use
Chart Type
Pie Chart
Pyramid Chart

Funnel Chart

Treemap

Studying the distribution of data
When to Use
Chart Type
Scatter plot

Bubble Chart

Error Chart

Heatmap

Displaying project data
When to Use
Chart Type
Gantt chart

Resource chart

Evaluating performance data
When to Use
Chart Type
Bullet chart

Linear Gauge
Circular Gauge

Exploring Geographical Data
When to Use
Chart Type
Choropleth Map
Dot Map
Bubble Map
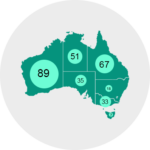
Connector Map
The Takeaway
As you would have guessed by now, when it comes to Data Viz, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. It requires a balance between the knowledge of what to use and the art of when to use it. Using our simple but practical guide, you should now have achieved that perfect balance and be ready to whip up the best chart for your data. Right? If you are still a wee bit confused and would instead leave the charts for the pros to handle, don’t worry, we have you covered. ScaleFresh excels at taking your data and turning it into an insightful asset. We work with various Data Viz tools, including Tableau and PowerBi, and can help you navigate these un‘chart’ed territories. Let us bring to life the story behind your data with our visuals.

By analyzing won and lost deals, we provided insights for offering the right discounts, resulting in reduced non-standard discounts and improved ARR.

Whether you’re a business user newly learning SQL or a Data Analyst who is already a pro, it never hurts to keep a handy reference guide for a quick peek the next time you’re writing an SQL query!

Built a support dashboard to visualize customer support metrics for the client’s end customers, enabling them to understand better the value of excellent support offered.

